Tag: Empathy
The Golden Rule is Making the World Worse


—
The Golden Rule — treat others as you would like others to treat you — is well intentioned in that it asks us to extend fairness and respect to others. But the outcomes are not necessarily good.
—
The problem is that it is based on a fundamentally flawed assumption.
—
The assumption that you want what I want, that fairness and respect mean for you what they mean for me. And this is rarely true. This is particularly relevant given the evils caused by the racism and the violence we’re seeing these days.
It is so easy to fall into the trap of assuming my way is the right way, and then to treat others as I think I should, without taking into account what they want. This is dangerous because it can make them feel disrespected and I might end up resenting the fact that they are being unappreciative of my efforts.
And we don’t have to go halfway across the world to make a difference. This applies to how we treat people at work, at home, on the streets, and in social media. Lest we come across as jerks, we want to be careful NOT to treat others like we would like them to treat us, unless we’re sure that is what they really want.
—
Never assume you know what others want. The alternative is to practice empathy.
—
The golden art of putting ourselves in their shoes to figure out how they would like to be treated. And we will probably be surprised by how much that can differ from what we expected to be appropriate.
If we are going to build a more fair, generous and compassionate world, we’re going to need a better rule. Here’s an iteration:
—
THE GOLDEN RULE 2.0
Treat others as THEY would like to be treated.
—
#BlackLivesMatter
Be. A message for leaders in confinement.

13 public speakers, members of keynoteboutique.com, join rhetorical forces to bring you a comforting message in these challenging times.
—–
—
Music by Alexander Nakarada | https://www.serpentsoundstudios.com
Feedback Part II: How to Encourage the Listener

Humans need feedback to grow, which make giving feedback the gift of growth. While positive feedback gives us the energy to grow, constructive feedback — when done well — shows us the path for growth, that is, what we can improve and how.
This series focusses on how we can make our constructive feedback more effective.
In part II, I share three ways to encourage the listener when we give constructive criticism.
What techniques do you use to encourage your listener?
—
How to Leave A First Good Impression

Darrell is a polite, handsome man, who had little luck meeting people and making friends. He didn’t get why and it was frustrating. I first met Darrell during his final months in prison — a few of robberies and a bad temper had got him into trouble.
But Darrell is one of the few who manage to overcome the nasty effects of jail time. He decided to change. And he did. What didn’t change was the way people reacted to him. It seemed as though everyone knew his past. Then he figured out why.
And it had nothing to do with his past.
.
People won’t figure out your past by looking at you.
But they’ll read your present in just a glance.
People won’t figure out your past by looking at you.But they’ll read your present in just a glance.It was actually quite obvious and he felt stupid for not figuring it out earlier. Back in the day, Darrell had the side of his neck tattooed with the universal “F*** YOU”. It was small but nonetheless LOUD!
He had it for so long, he no longer noticed it — Gosh, I no longer noticed it and I hadn’t known him for that long. But for people who didn’t know him it was a big thing. Obviously! It automatically kept everyone away, giving him no chance to interact.
So Darrell covered it with a new tattoo. And the next time we met… he was smiling.
Don’t be surprised at the way people react to you
when your face is telling them just how you feel.
We might not have tattoos on our neck, but our facial expression and body language are tattoos we carry around always. They provide universal information before we speak. The way you look, move and talk are the first signals other people pick up.
In the art of human relations, this is nothing new. However, we’re not always aware of how we read these signs automatically (and sometimes unconsciously) and how others do too.
There’s never a second chance to leave a first good impression.
Do you sometimes feel a bit concerned about leaving the right impression or little uneasy when meeting people for the first time? I do. But think about it: other people do too. Chances are they’re busy thinking about themselves, not about you!
So before I step in, I make a conscious decision to step away from this trap, and think: These are people, not monsters. And they’re in the same situation as me.
If you’d like people to walk away thinking: “Well, that was pleasant. Seems like a nice person. What conviction!” here’s a tip:
Your best business card is YOU. Make sure you look the way you want others to see you. Stand tall. Radiate determination and serenity with every step. Smile. Make eye contact. Smile. Speak with a clear, confident voice. Smile.
Love to hear what you do to leave a lasting first good impression?
The Difference Between Sympathy And Empathy

Today I read a post on LinkedIn written by John Ford about the difference between sympathy and empathy. I decided to comment on it, but the amount of text seems to be limited. So I wrote this post instead.
Words matter. Agreeing on what words mean matters more.
The Ancient Greek words for sympathy and empathy (which then found their way into Latin) can provide insight into to their meaning today.
They have a common root, the “pathy” part. It derives from the Greek word “pathos” (πάθος), which means “pain, suffering, passion”.
Prefixed to the root are conjunctions: “sym” meaning “with” (from “sun”, σύν) and “em” meaning “in” (from “en”, ἐν). This adds up to:
Sympathy is “pain with”: to feel the pain with someone.
Empathy is “pain in”: to feel the pain in someone.
Sympathy, in its positive understanding, means we identify with the person’s pain because we’ve experienced the same or a similar situation.
Empathy takes it up a notch: we feel the person’s pain, even though we do not personally relate to their situation. In other words:
Sympathy is putting yourself in someone’s shoes and feeling:
“I know what it’s like, mine feel the same.”
Empathy is putting yourself in someone’s shoes and feeling:
“I don’t know what it’s like, mine feel nothing like that. But I relate to how they make you feel.”
Empathy is priceless when we’re incapable of identifying with the person, for instance, when people do things we could never picture ourselves doing.
Empathy allows us to connect with them by identifying with their feelings and emotions, even though we consider their actions and behavior unacceptable.
12 Tips For Constructive Feedback
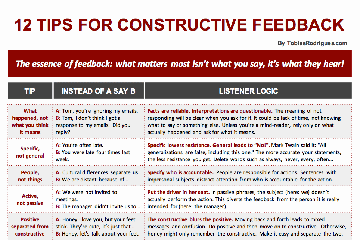
Whether a direct report, a manager, a colleague, a friend or a partner, giving constructive feedback is a crucial element of our relationships.
.
How you give feedback
determines how it is received.
I moderate constructive feedback sessions for teams and their leaders, and some patterns prove to be more effective than others. Here’s a set of keys that unlock the doors for constructive feedback to be well received.
Download and discuss them with those you give feedback to.
What matters most
isn’t what you say, it’s what they hear.
So by all means, I’d love to hear your constructive feedback.
Is Your Small Talk SMART?

Last week I attended the 3rd Hola Barcelona Cocktail, an event organized by Barcelona Global to welcome new international professionals arriving in Barcelona.
The purpose is to strengthen the relationship between Barcelonians by birth and Barcelonians by choice. It was lovely. I met wonderful people and conversations were great, which got me thinking: What makes small talk interesting?
The topic is important, but not everything — you can have a pointless conversation about a great topic! The key is HOW we talk.
Make small talk SMART:
Supportive, Meaningful, Authentic, Refreshing, and Tasteful
But, is small talk really that important? After all, it’s just chit-chat, right? Or not? Is there a connection between small talk and other areas of our life?
As a team effectiveness trainer, I often join teams for social events after the training. And for 4 years now I’ve been looking for a connection between the quality of small talk and people’s professional and personal fulfillment. I’ve found one:
Effective leaders and teams engage in smart small talk.
There’s a chance I’m seeing what I want to see, which begs the question: Is there scientific evidence to support my findings? I did some digging and there is.
For instance, Judith E. Glaser has coined the term “Conversational Intelligence” or “C-IQ”, a person’s ability to connect with others through conversations and to jointly think innovatively, empathetically, creatively and strategically.
Judith and the people at Benchmark Communications Inc. have studied the neurochemistry of conversations and shown that managers who “talk smart” are more successful than those who don’t.
So small talk is not just a chit-chat. Smart small talk does make a difference!
Here’s an experiment to spice up conversations at your next event:
- Step One: Identify interesting angles to the conversation, relevant aspects or perspectives that are being overlooked.
- Step Two: Ask a politely provocative question. This will accomplish two things: you’ll get people’s attention and you’ll spark openings for more meaningful dialogue.
- Step Three: Pick a positive message. This is important because you want to contribute to the conversation in meaningful way.
Easy to remember: Angle + Question + Message.
What do you do to keep the small talk smart?
The Trust Story

This meant he didn’t really trust anyone.
Except for one person: his special friend. It took him more than 10 years to do so. Before trusting him, he assessed the events that indicated his special friend was worthy of trust:
– When I wanted to go for a drink, my friend was always ready.
– When I renovated my apartment, my friend booked all his weekends until it was done.
– Even when I considered a career change, my friend was there to carefully listen and give good advice.
– And when my mom died, my friend never once left my side.
For the first time the man felt he was ready to trust.
The next day, his special friend died.
For the remainder of his days, the man wondered if his friend had also trusted him. And when they met in the afterlife, the first thing the man did was ask his friend if he had been trustworthy, and if so, when had he decided to trust him.
Staring at the man with a look of confusion on his face, the special friend said:
Of course you’re my trusted friend! I decided to trust you the day we met. And ever since you’ve never betrayed my trust:
– Whenever you needed a favor, you trusted me to ask for help.
– When you wanted to go for a drink, it was me who you choose to confide your secrets.
– When you renovated your apartment, you allowed me and no other to enter the privacy of your home to rebuild it.
– Even that time — remember? — when you were considering a career change, again it was me who you turned to for advice.
– And when your mom passed, I was the only one you accepted at your side.
Your actions have taught me the meaning of trust!
The man stood there in shock, thinking:
You never fully know what people are capable of. By this token, you’ll never really know when you can trust someone.
Credits: I first heard of a credit for trust from my dear friend Florian Mueck.
The Connection Matrix – Part One
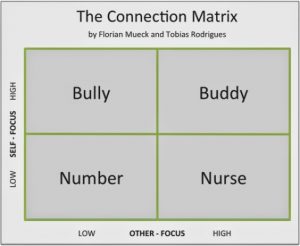
The other day I was sitting on a plane from Warsaw to Barcelona. With me, my friend, speaker and trainer Florian Mueck. We were coming back from a spectacular Spectacular Speaking event.
In her opening speech, the incomparable Olivia Schofield, founder of the Spectacular Speaking series, said: The one thing that takes you from great to spectacular is… connection. Connection. Connection between the speaker and the audience. Connection between oneself and the other.
Florian and I started to philosophize about this subject. We played around with different dimensions and combinations and patterns. We scribbled and painted and drew and scribbled…
In the end, we knew that we wanted to show two dimensions – the self-focus (or speaker focus) and the other-focus (or audience focus). Self/other-focus refers to the degree with which one chooses to be concerned with oneself and with others.
We also knew that we wanted to use the high-low categories. Our big challenge – the four field titles. After three hours we finally felt confident about the names. “The Connection Matrix” was born.
The Connection Matrix shows four different kinds of speakers/communicators. In this first part we’ll look at the status quo of their communication mode.
Number – Low Other/Low Self
Low empathy combined with low self-interest. Numbers drive through life with their handbrake on. They’re the typical business presenters. Not passionate about the data they present, numbers deliver only to deliver. Their voice? Monotonous. Their body language? Closed. Their enthusiasm? Not existent.
They say: But how can I put passion into my monthly business unit report? Numbers never consider a speech or presentation an opportunity. For them, communication is an obligation. Creativity is for artists, they think.
They also think: I do my job. Isn’t that enough? If others don’t like what I say, it’s not my fault. Numbers are brilliant at avoiding responsibility – for themselves and the audience. Like Florian’s mom says: Where there’s no hook, you cannot hang a jacket.
The paradox with numbers is that they don’t count: no one listens, no one remembers, no one cares. Connecting as number, you fail to connect. Number-mode is beneficial only when you wish not to connect. Numbers are the poorest connectors of the four types.
Nurse – High Other/Low Self
High empathy combined with low self-interest. Nurses strive to please their audience. They communicate with the language of “you” and their goal is to promote the audience. A nurse’s communication style consists of satisfying the interests of others.
The paradox with nurses is that by failing to affirm their self-interests, the connection entails no expense and so is undervalued. Because nurses don’t speak up for themselves, audiences don’t really listen, care less and very easily forget.
Connecting as a nurse, you don’t make an impact. Nurse-mode is beneficial when you wish to go unnoticed. If you don’t shift to buddy, your audience will soon take you for granted!
Bully – Low Other/High Self
Low empathy combined with high self-interest. Bullies strive to satisfy their own interests. Bullies communicate with the language of “I” and their style consists of pushing an agenda.
In bully-mode, you believe only you hold the power to make a change. So you feel you have little to learn from your audience. A bully’s preferred strategy is Follow me, now!
The paradox with bullies is that in failing to give the recognition they seek, they struggle all the more to get it from their audience. People listen, they remember, oh! but they don’t care.
Connecting as a bully, you fail to inspire trust. Bully-mode is beneficial when all you want is to stand out from the crowd. If you don’t shift to buddy, your audience will begin to feel betrayed and soon you’ll end up talking to yourself!
Buddy – High Other/High Self
High empathy combined with high self-interest. Buddies strive to develop a whole that is greater than the sum of its parts. Buddies communicate with the language of “we” and their style consists of promoting ways to satisfy self-interests and the interests of others.
In buddy-mode, you believe in a joint potential and so the purpose of communicating is mutual growth. The preferred strategy is How shall we do this? You know you’re listening to a buddy when you’re pushed out of your comfort zone and it feels good!
The paradox with buddy-mode is that when you place the connection at the center, the result is the speaker meets her goals and the audience gets what they came for. Everyone is happy. Audiences remember buddies, they listen to them, and they definitely care.
Connecting as a buddy, you act like a magnet, attracting others to move out their communication mode and to connect as buddies. Buddy is the ultimate mode of connection because everyone grows beyond expectation.
Whether you consider yourself a Number, a Nurse or a Bully, in The Connection Matrix – Part Two we’ll share with you insights on how to become a Buddy, the ultimate connector.
Rage Against The Dying Of The Light

In this poem “Do Not Go Gentle Into That Good Night”, Welsh poet and writer, Dylan Thomas proclaims that the wise and good do not go gently into the good night of death.
Instead, they rage against the dying of the light, against the demise of what wisdom and good their words and deeds may have effected in the world.
Though good and wise leaders must die, as we all,
their light need not follow them into the good night.